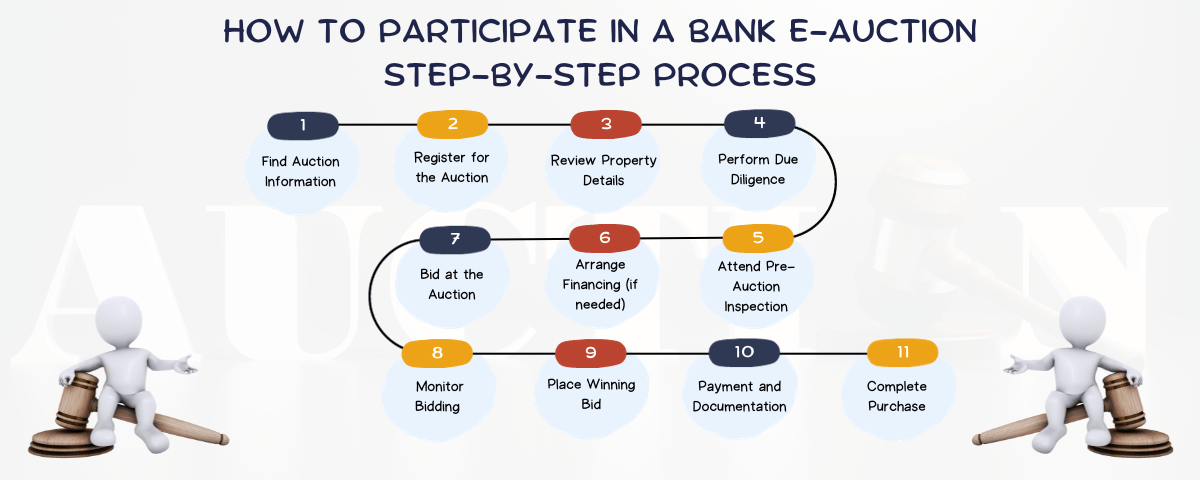
To participate in a bank e-auction, you can follow these steps:
Identify the bank whose e-auction you want to participate in: You can visit the website of the bank or check with their nearest branch to find out about upcoming e-auctions.
Register on the bank's e-auction portal: Most banks have an online portal where you can register as a bidder.
Also you can check out: Github on Eauction Process
Properties are auctioned by banks for several reasons, primarily related to the recovery of unpaid loans and the management of distressed assets. Here are some of the key reasons why banks auction properties:
Loan Default: When individuals or businesses borrow money from a bank to purchase a property and fail to repay the loan or meet their mortgage obligations, the property becomes collateral for the loan. If the borrower defaults on the loan, the bank has the right to seize and sell the property to recover the outstanding debt.
Non-Performing Assets: Banks aim to maintain a healthy loan portfolio, and non-performing assets (NPAs) can negatively impact their financial health. To minimize the impact of NPAs on their balance sheets, banks often take steps to recover the loan amount, including selling the collateral property through auctions.
Timely Recovery: Banks prefer to recover their loan amounts as quickly as possible. Auctioning a property allows them to expedite the recovery process, rather than going through lengthy legal procedures, such as foreclosure.
Minimizing Holding Costs: Holding onto a foreclosed property can be costly for a bank. They must bear expenses related to property maintenance, property taxes, and insurance while the property is in their possession. Auctioning the property helps minimize these holding costs.
Liquidity: Banks are in the business of lending money, not managing real estate properties. Auctioning properties allows them to convert illiquid assets (real estate) into cash, which they can then use for lending or other investments.
Fair Market Value: Auctions are often seen as a transparent way to determine the fair market value of a property. This ensures that the bank gets the best possible price for the property and maximizes its chances of recovering the outstanding loan amount.
Legal Requirement: In many jurisdictions, banks are legally required to follow a specific process to recover loans secured by real estate. This process often includes auctioning the property as a final step after attempts to negotiate with the borrower have failed.
Avoiding Property Depreciation: Real estate values can fluctuate, and properties can deteriorate over time if not properly maintained. Selling the property through an auction allows banks to avoid potential depreciation and associated losses.
Buying a bank auction property in India can offer several advantages, but it also comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. Here are some reasons why individuals may choose to buy a bank auction property in India:
Potential for Below-Market Prices: Bank auction properties are often sold at a discount compared to their market value. This can provide an opportunity for buyers to acquire a property at a relatively lower cost.
Transparent Process: Auctions conducted by banks are typically transparent and follow a well-defined process, which can provide a sense of security to buyers.
Diverse Property Options: Bank auctions can include a variety of property types, including residential, commercial, and agricultural properties. This diversity allows buyers to explore different investment opportunities.
No Property Chain: Since the property is being sold by the bank, there is usually no property chain involved, reducing the risk of delays or complications associated with multiple transactions.
Clear Title: Banks typically ensure that the property being auctioned has a clear title, reducing the risk of legal disputes over ownership.
Financing Options: Some banks may offer financing options for auction properties, making it easier for buyers to secure funding.
Investment Opportunity: Buying an auction property can be an attractive investment opportunity, especially for those looking to enter the real estate market or expand their property portfolio.
Renovation and Flipping Potential: Auction properties are often sold as-is, which means buyers may have the opportunity to purchase a property that requires renovation or improvement. This can be appealing for individuals interested in flipping properties or adding value through renovations.
However, it's important to note that buying a bank auction property in India also comes with certain risks and challenges:
Limited Inspection Time: Buyers may have limited time to inspect the property before the auction, which can make it difficult to assess its condition thoroughly.
Competitive Bidding: Auctions can be competitive, with multiple buyers vying for the same property. This can drive up the final selling price.
Outstanding Dues and Liabilities: Buyers must carefully research the property's history to determine if there are any outstanding dues, taxes, or liabilities associated with it.
Legal Considerations: Legal procedures related to bank auction properties can be complex, and buyers should seek legal advice to ensure they understand the implications of the purchase.
Financing Challenges: Securing financing for auction properties can sometimes be more challenging than traditional property purchases.
Risk of Delays: Despite a transparent process, bank auctions can sometimes face delays or legal challenges, which can impact the timing of property acquisition.
The property bank auction process in India involves several steps and procedures that are governed by the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002, and various regulations and guidelines issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Below is an overview of the key steps involved in the bank auction process in India:
Loan Default by Borrower:
Issue of Notice by the Bank:
Response from Borrower:
Possession Notice:
Valuation of the Property:
Public Notice of Auction:
E-auction (Online Auction):
Bidding Process:
Winning Bidder:
Sale Certificate:
Possession of Property:
Transfer of Title:
Buying a bank auction property in India can be a lucrative investment opportunity, but it comes with its own set of risks and challenges. Here are some important points to remember when considering the purchase of a bank auction property in India:
Due Diligence: Thoroughly research the property you intend to bid on. This includes inspecting the property, checking its legal status, verifying ownership, and understanding any pending dues, encumbrances, or disputes associated with it.
Financial Readiness: Ensure you have the necessary funds or financing in place before participating in the auction. Be prepared to pay the earnest money deposit and the full purchase price as per the auction terms.
Auction Notice: Carefully review the auction notice, which contains important details about the property, the reserve price, the auction date, and the terms and conditions of the auction.
Legal Advice: Seek legal advice to understand the legal implications of buying a bank auction property. A lawyer can help you navigate the complex legal procedures and ensure that you are protected.
Earnest Money Deposit: Be aware of the earnest money deposit requirement. This is typically a percentage of the reserve price, and you'll need to pay it to participate in the auction. Ensure you have the funds ready.
Bidding Strategy: Decide on your bidding strategy in advance. Determine your maximum bid amount based on your budget and the property's market value. Stick to your budget to avoid overpaying.
Competition: Be prepared for competition. Auctions can be competitive, and multiple bidders may be interested in the same property.
Financing: If you plan to take a loan to purchase the property, make sure you have pre-approval from a lender. Financing for auction properties can be more challenging to secure compared to regular property purchases.
Payment Timeline: Understand the payment timeline specified in the auction notice. Typically, you'll need to make the full payment within a specified period after winning the auction.
Hidden Costs: Be aware of additional costs associated with the purchase, such as stamp duty, registration fees, transfer charges, and any outstanding dues or taxes on the property.
Possession: Determine when you can take possession of the property and factor this into your plans. The possession process may take time, especially if the property is occupied.
Legal Clearance: Ensure that the property has a clear title and is free from any legal disputes. You don't want to inherit someone else's legal problems.
Registration: After winning the auction, complete the registration of the property in your name. This involves legal documentation and payment of registration fees.
Resale Value: Consider the potential resale value of the property and its location. Evaluate the long-term investment prospects.
Patience and Persistence: The bank auction process can be lengthy and complex. Be patient and persistent throughout the process.
Documentation: Keep all relevant documents, receipts, and communication related to the auction and the property purchase for future reference.
Post-Purchase Responsibilities: After acquiring the property, be prepared to handle maintenance, property taxes, and other ongoing responsibilities associated with property ownership.